What is Microsoft Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program that is used to record and analyse numerical data. Think of a spreadsheet as a collection of columns and rows that form a table. Alphabetical letters are usually assigned to columns and numbers are usually assigned to rows. The point where a column and a row meet is called a cell. The address of a cell is given by the letter representing the column and the number representing a row. Let's illustrate this using the following image.
Why Should I Learn Microsoft Excel?
We all deal with numbers in one way or the other. We all have daily expenses which we pay for from the monthly income that we earn. For one to spend wisely, they will need to know their income vs. expenditure. Microsoft Excel comes in handy when we want to record, analyze and store such numeric data.
Where can I get Microsoft Excel?
There are number of ways in which you can get Microsoft Excel. You can buy it from a hardware computer shop that also sells software. Microsoft Excel is part of the Microsoft Office suite of programs. Alternatively, you can download it from the Microsoft website but you will have to buy the license key.
How to Open Microsoft Excel?
Running Excel is not different from running any other Windows program. If you are running Windows with a GUI like (Windows XP, Vista, and 7) follow the following steps.
- Click on start menu
- Point to all programs
- Point to Microsoft Excel
- Click on Microsoft Excel
Alternatively, you can also open it from the start menu if it has been added there. You can also open it from the desktop shortcut if you have created one.
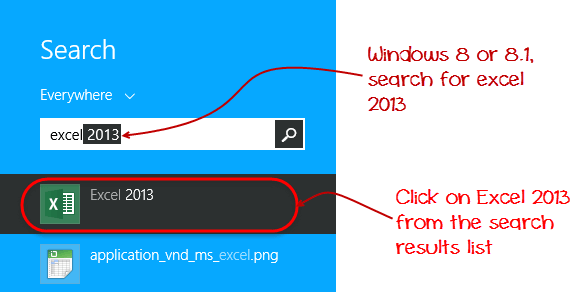
For this tutorial, we will be working with Windows 8.1 and Microsoft Excel 2013. Follow the following steps to run Excel on Windows 8.1
- Click on start menu
- Search for Excel N.B. even before you even typing, all programs starting with what you have typed will be listed.
- Click on Microsoft Excel
The following image shows you how to do this
Understanding the Ribbon
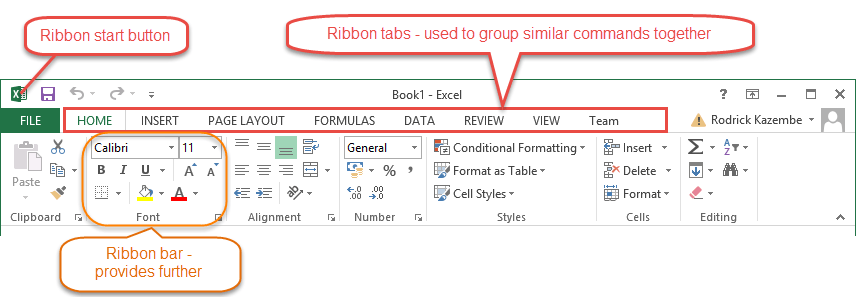
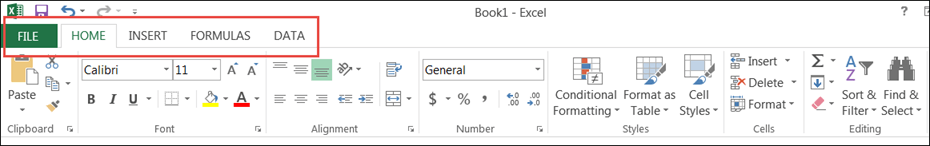
The ribbon provides shortcuts to commands in Excel. A command is an action that the user performs. An example of a command is creating a new document, printing a documenting, etc. The image below shows the ribbon used in Excel 2013.
Ribbon components explained
Ribbon start button - it is used to access commands i.e. creating new documents, saving existing work, printing, accessing the options for customizing Excel, etc.
Ribbon tabs – the tabs are used to group similar commands together. The home tab is used for basic commands such as formatting the data to make it more presentable, sorting and finding specific data within the spreadsheet.
Ribbon bar – the bars are used to group similar commands together. As an example, the Alignment ribbon bar is used to group all the commands that are used to align data together.
Understanding the worksheet (Rows and Columns, Sheets, Workbooks)
A worksheet is a collection of rows and columns. When a row and a column meet, they form a cell. Cells are used to record data. Each cell is uniquely identified using a cell address. Columns are usually labelled with letters while rows are usually numbers.
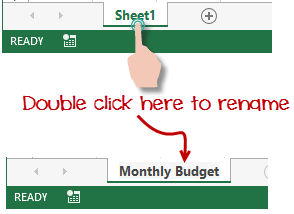
A workbook is a collection of worksheets. By default, a workbook has three cells in Excel. You can delete or add more sheets to suit your requirements. By default, the sheets are named Sheet1, Sheet2 and so on and so forth. You can rename the sheet names to more meaningful names i.e. Daily Expenses, Monthly Budget, etc.
Customization Microsoft Excel Environment
Personally I like the black colour, so my excel theme looks blackish. Your favourite colour could be blue, and you too can make your theme colour look blue-like. If you are not a programmer, you may not want to include ribbon tabs i.e. developer. All this is made possible via customizations. In this sub-section, we are going to look at;
- Customization the ribbon
- Setting the colour theme
- Settings for formulas
- Proofing settings
- Save settings
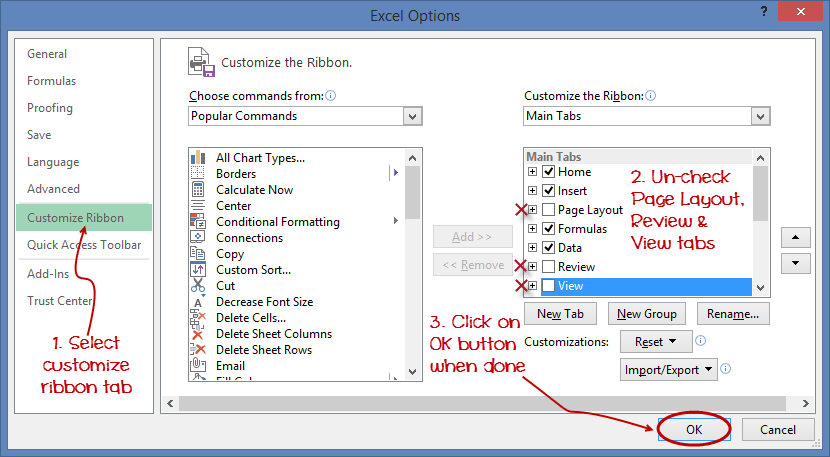
Customization of ribbon
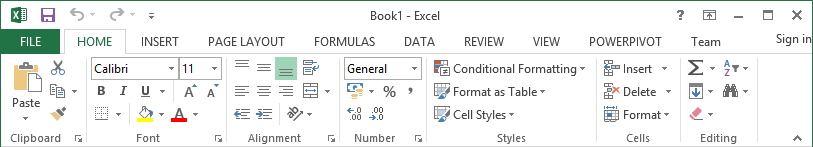
The above image shows the default ribbon in Excel 2013. Let's start with customization the ribbon, suppose you do not wish to see some of the tabs on the ribbon, or you would like to add some tabs that are missing such as the developer tab. You can use the options window to achieve this.
- Click on the ribbon start button
- Select options from the drop down menu. You should be able to see an Excel Options dialog window
- Select the customize ribbon option from the left-hand side panel as shown below
- On your right-hand side, remove the check marks from the tabs that you do not wish to see on the ribbon. For this example, we have removed Page Layout, Review, and View tab.
- Click on the "OK" button when you are done.
Your ribbon will look as follows
Adding custom tabs to the ribbon
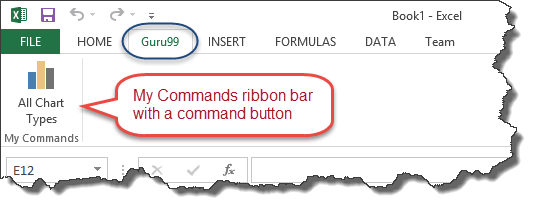
You can also add your own tab, give it a custom name and assign commands to it. Let's add a tab to the ribbon with the text Guru99
- Right click on the ribbon and select Customize the Ribbon. The dialogue window shown above will appear
- Click on new tab button as illustrated in the animated image below
- Select the newly created tab
- Click on Rename button
- Give it a name of Guru99
- Select the New Group (Custom) under Guru99 tab as shown in the image below
- Click on Rename button and give it a name of My Commands
- Let's now add commands to my ribbon bar
- The commands are listed on the middle panel
- Select All chart types command and click on Add button
- Click on OK
Your ribbon will look as follows
Setting the colour theme
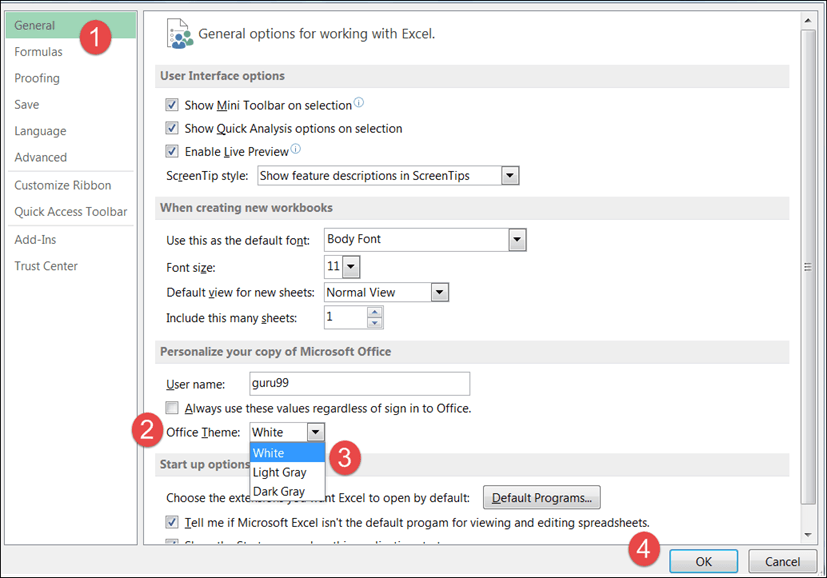
To set the color-theme for your Excel sheet you have to go to Excel ribbon, and click on à File àOption command. It will open a window where you have to follow the following steps.
- The general tab on the left-hand panel will be selected by default.
- Look for colour scheme under General options for working with Excel
- Click on the colour scheme drop-down list and select the desired colour
- Click on OK button
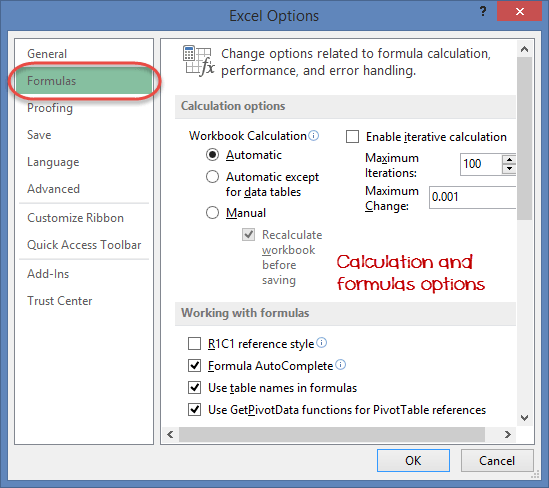
Settings for formulas
This option allows you to define how Excel behaves when you are working with formulas. You can use it to set options i.e. autocomplete when entering formulas, change the cell referencing style and use numbers for both columns and rows and other options.
If you want to activate an option, click on its check box. If you want to deactivate an option, remove the mark from the checkbox. You can this option from the Options dialogue window under formulas tab from the left-hand side panel
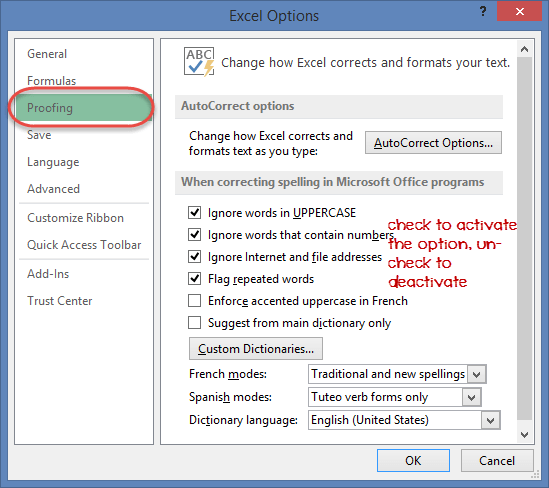
Proofing settings
This option manipulates the entered text entered into excel. It allows setting options such as the dictionary language that should be used when checking for wrong spellings, suggestions from the dictionary, etc. You can this option from the options dialogue window under the proofing tab from the left-hand side panel
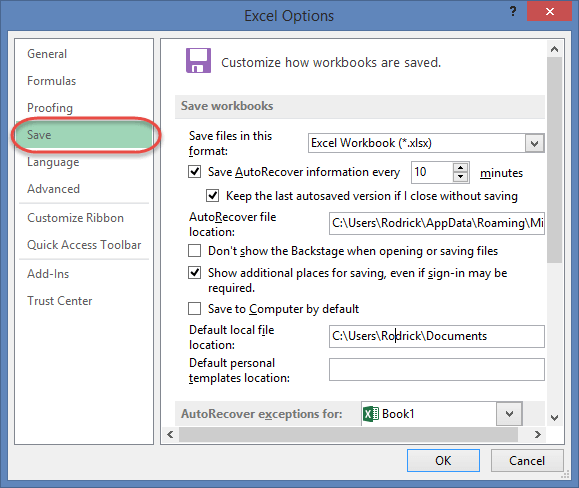
Save settings
This option allows you to define the default file format when saving files, enable auto recovery in case your computer goes off before you could save your work, etc. You can use this option from the Options dialogue window under save tab from the left-hand side panel
Important Excel shortcuts
| Ctrl + P | used to open the print dialogue window |
| Ctrl + N | creates a new workbook |
| Ctrl + S | saves the current workbook |
| Ctrl + C | copy contents of current select |
| Ctrl + V | paste data from the clipboard |
| SHIFT + F3 | displays the function insert dialog window |
| SHIFT + F11 | Creates a new worksheet |
| F2 | Check formula and cell range covered |
Best Practices when working with Microsoft Excel
- Save workbooks with backward compatibility in mind. If you are not using the latest features in higher versions of Excel, you should save your files in 2003 *.xls format for backwards compatibility
- Use description names for columns and worksheets in a workbook
- Avoid working with complex formulas with many variables. Try to break them down into small managed results that you can use to build on
- Use built-in functions whenever you can instead of writing your own formulas






No comments:
Post a Comment